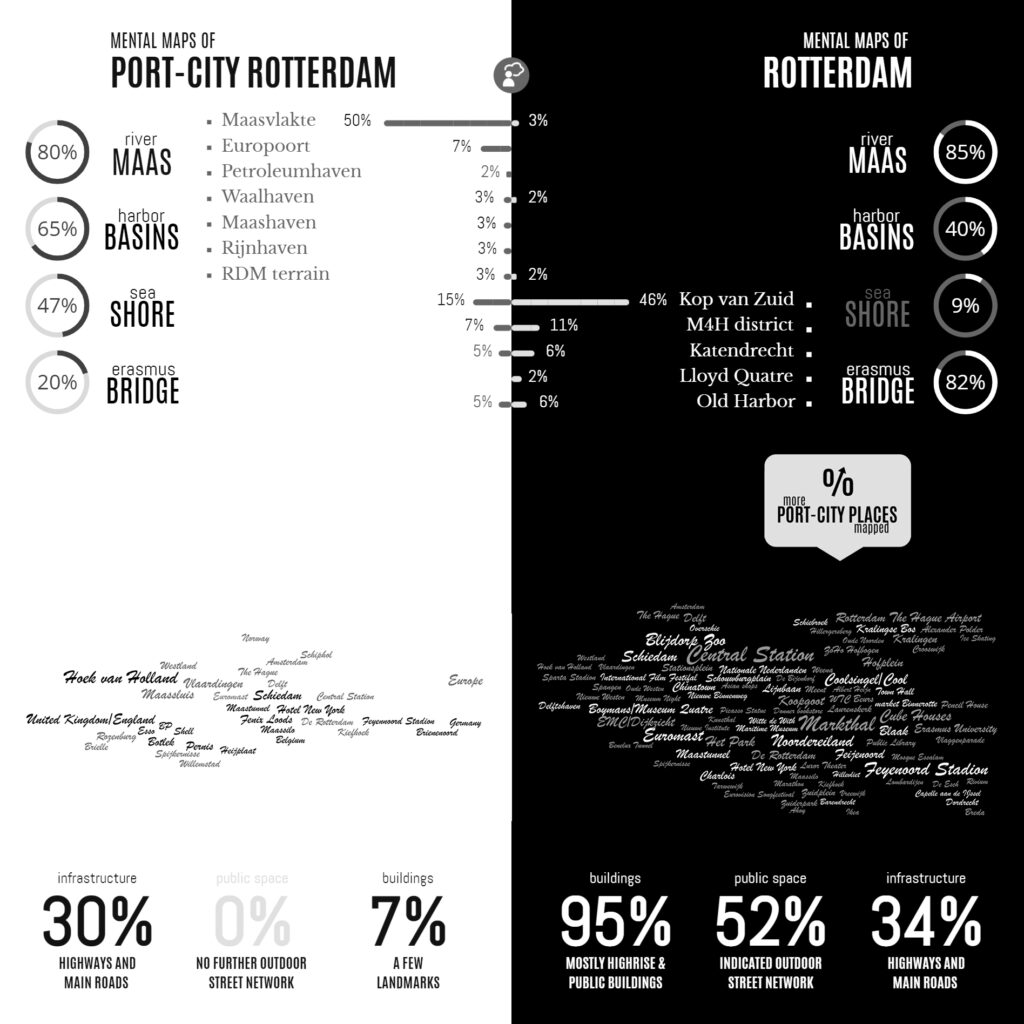
Infographic of the Comparative Analyses on the two Sets of Mental Maps
In the Minds of People: The Case of Rotterdam
Following the geographical ‘Any-Port Model’, urban design has stipulated and enforced the disunion of port and city over the recent decades. In conjunction with other disciplines, the emphasis has been laid at the dislocation of production activities in favour of logistic-productive dynamics. At the same time, the professional focus was on the urban areas where most citizens are. While this practice has led to the redevelopment of abandoned harbour areas too, foremost the approach stimulated stronger physical boundaries between lived city and the remaining and new harbour areas. This article describes the application of the dominant model in Rotterdam over the recent decades, on the basis of literature review, and, it confronts this with the concepts of Rotterdam which are in the minds of professionals-in-training, through the method of ‘mental mapping’. On the one hand, mainly harbour areas are memorised when respondents are asked to draw the port-city of Rotterdam, even though its efficient port infrastructure makes public space in these areas rare, and most harbours are located behind inaccessible borders. On the other hand, civic areas, which have a refined network of public spaces and are places for daily life, reveal also all kinds of tangible and intangible signs and symbols related to characteristics of the port-city when memorised; even more. Various elements, linked to water-land or the flows of goods, people, and ideas, dominate the minds of the people when they think of Rotterdam in general. These outcomes reconfirm the unique unity of port and city and provide a way to find an alternative or supplementary model accepting the complex nature of port-cities.
Read:
Harteveld, Maurice (2021) In the Minds of People: Port-City Perspectives, The Case of Rotterdam, In: European Journal of Creative Practices in Cities and Landscapes (CPCL), Vol. 4, No. 2.
See also:
Maritime Mindsets
Biographies of Places


 On the occasion of its Dies Natalis celebration, the Delft University of Technology together with the Delft Design for Values Institute has organised a symposium on Design for Values.
On the occasion of its Dies Natalis celebration, the Delft University of Technology together with the Delft Design for Values Institute has organised a symposium on Design for Values.
