How to Design Public Space for Maritime Mindsets? That’s a central question in the new Minor ‘Minor (Re)Imagining Port Cities: Understanding Space, Society, and Culture’.
Tag Archives: public opinion
Waterfront as Environmental Infrastructure
The waterfront is a fragile and thin marginal area where multiple interactions occur between the city and the water. It is not a border or a limit. On the contrary, it is a meeting space, an interchange area, a transition – and tension – between different biological communities. Like all environmental frontiers, the waterfront is an ecosystem with a dynamic and precarious balance. Water-related challenges such as protection from wave motion, and adaptation to multiple conditions (e.g. hydrogeological, health, and environmental risks), albeit relevant, are often addressed in a sectorial way through confusing and ineffective procedures and plans. The centrality that the environment assumes in the transformation processes of the land-water interfaces requires the preparation of a design approach that aims to operate as a device capable of providing a response to social and ecological rebalancing, in terms of resilience as well as energy efficiency, reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and environmental safety. Urban design solutions need to consider the availability of resources; social-environmental changes are confronted with the long time of ecological-environmental processes and adaptations. At the same time, targeted interventions correlate with the many ongoing and planned activities in the specific territories.
According to this approach, the concept of a waterfront becomes an environmental infrastructure, overcoming obsolete ideas of waterfronts as purely related to commercial development. The design of a waterfront is incremental and inter-scalar and it considers the risks and socio-ecological environmental fragility of coastal territories as priority themes to trigger urban, and territorial, regeneration.
Faculty of Architecture, TU Delft
September 8, 2022
15:00-17:00h
Matteo Di Venosa (speaker)
Carola Hein (discussants)
Paolo De Martino
Elise van Dooren
Maurice Harteveld
Port-City Perspectives
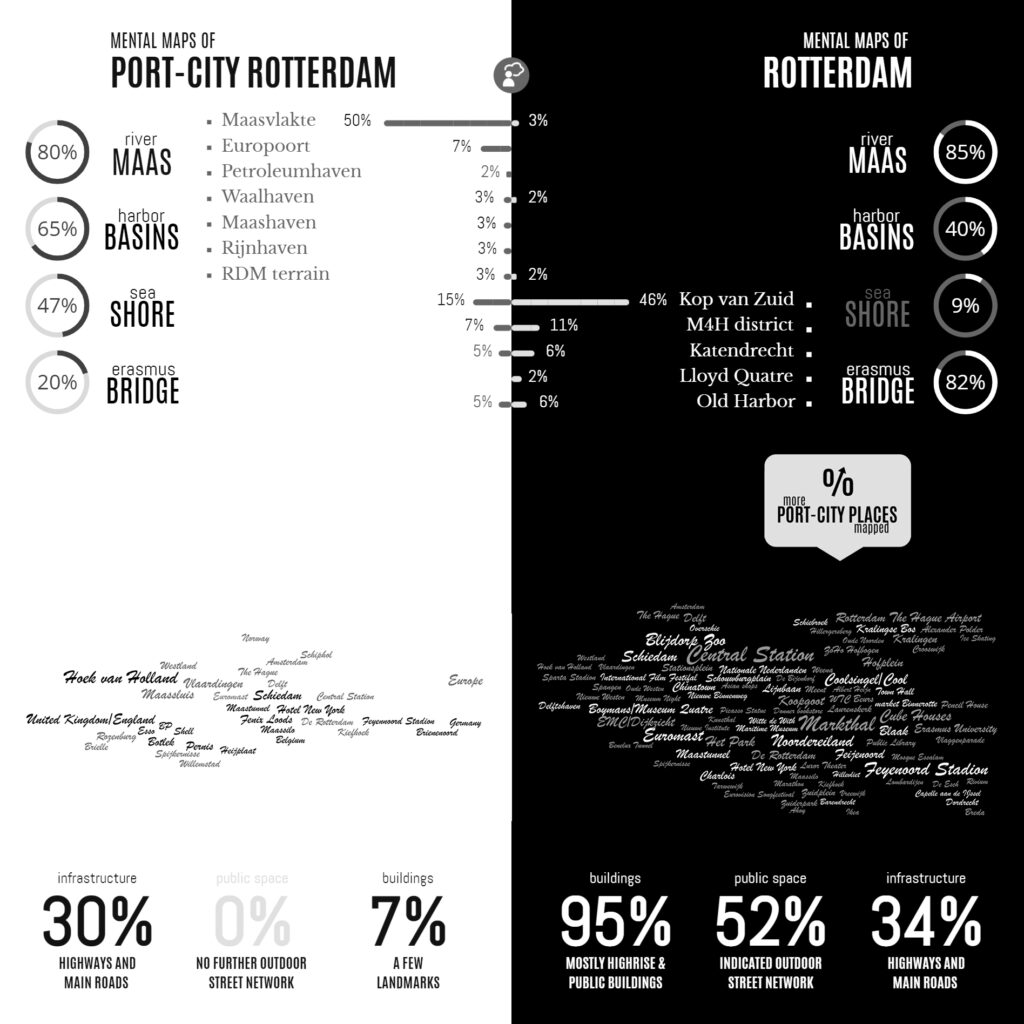
Infographic of the Comparative Analyses on the two Sets of Mental Maps
In the Minds of People: The Case of Rotterdam
Following the geographical ‘Any-Port Model’, urban design has stipulated and enforced the disunion of port and city over the recent decades. In conjunction with other disciplines, the emphasis has been laid at the dislocation of production activities in favour of logistic-productive dynamics. At the same time, the professional focus was on the urban areas where most citizens are. While this practice has led to the redevelopment of abandoned harbour areas too, foremost the approach stimulated stronger physical boundaries between lived city and the remaining and new harbour areas. This article describes the application of the dominant model in Rotterdam over the recent decades, on the basis of literature review, and, it confronts this with the concepts of Rotterdam which are in the minds of professionals-in-training, through the method of ‘mental mapping’. On the one hand, mainly harbour areas are memorised when respondents are asked to draw the port-city of Rotterdam, even though its efficient port infrastructure makes public space in these areas rare, and most harbours are located behind inaccessible borders. On the other hand, civic areas, which have a refined network of public spaces and are places for daily life, reveal also all kinds of tangible and intangible signs and symbols related to characteristics of the port-city when memorised; even more. Various elements, linked to water-land or the flows of goods, people, and ideas, dominate the minds of the people when they think of Rotterdam in general. These outcomes reconfirm the unique unity of port and city and provide a way to find an alternative or supplementary model accepting the complex nature of port-cities.
Read:
Harteveld, Maurice (2021) In the Minds of People: Port-City Perspectives, The Case of Rotterdam, In: European Journal of Creative Practices in Cities and Landscapes (CPCL), Vol. 4, No. 2.
See also:
Maritime Mindsets
Biographies of Places
Mapping Maritime Mindsets: Mental Maps
Imagine: You are asked to draw a port city from memory. What would you put on paper? Do you think of harbours? Water, docks, cargo, moving loads, and ships? If your drawing shows these elements, don’t be surprised. Sixty-five graduate students also took on the challenge. In answering: “draw the port city of Rotterdam by mind”, the drawings of the participants (fig.1) displayed exactly the above features. Of course, this makes sense. A port just happens to be a place on the water in which ships shelter and dock to (un)load cargo and/or passengers. A harbour is a sheltered place too, and in its nautical meaning, it is a near-synonym for sheltered water, in which ships may dock, especially again for (un)loading. So, all the above linguistic lemmas are there and all these are connected to imaginable objects.
Keep reading on Port City Futures | Leiden•Delft•Erasmus
Public Space: Changing Values
The Quest for Public Space: Changing Values in Urban Design, The City as Learning Lab and Living Lab
This article highlights the dynamics of values in our reasoning on public space. By means of an epistemological study, it tests the contemporary premises underlying our ways to safeguard the inclusive, democratic, agential city, and, as such, it aims to update our view on urban design. The article raises three subsequent questions: [i] Is the city our common house as perceived from the Renaissance onward, containing all, and consequently are public spaces used by the people as a whole? [ii] Is the city formalising our municipal autonomy as emphasised since the Enlightenment, in an anti-egoistic manner, and in this line, are public spaces owned by local governments representing the people? And, [iii] is the city open to our general view as advocated in Modern reasoning, restricting entrepreneurial influences, and synchronically, is its public spaces seen and/or known by everyone? – Inclusiveness, democracy, agentiality are strongholds in our scientific thinking on public space and each issue echoes through in the practice on urban design. Yet, in an aim to keep cities connected and accessible, fair and vital, and open and social, conflicts appear. Primarily based upon reviewing urban theory and particularly experiencing the Amsterdam for this matter, the answering of questions generates remarks on this aim. Contemporary Western illuminations on pro-active citizens, participatory societies, and effects of social media and micro-blogging forecast a more differentiated image of public space and surmise to enforce diversification in our value framework in urban design.
See:
Harteveld, Maurice G. A. D. (2017) The Quest for Public Space: Changing Values in Urban Design, The City as Learning Lab and Living Lab, IN Tieben, Hendrik, Yan Geng, and Francesco Rossini (eds) The Entrepreneurial City, , Rotterdam: International Forum on Urbanism (IFoU) / Hong Kong: School of Architecture, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, pp. 395-411
or alternative link
10yrs of Graduation Projects
Liveability and Public Space in the Happy City
9th September 2015, 8:45-10:30h
Lecture
Delft University of Technology
Room: IO-Bernd Schierbeek
Landbergstraat 15
Delft
My faculty in Delft is one of the world’s largest in the field of architecture and urban design. “It is a place that is buzzing with life from early in the morning until late at night, with four thousand people studying, working, designing, conducting research and acquiring and disseminating knowledge*.” In this environment, I have supervised quite some graduates in their final master thesis, all focussed on liveability and public space. What can we learn from them and how to proceed?
Liveability and Public Space in the Happy City [download pdf]
