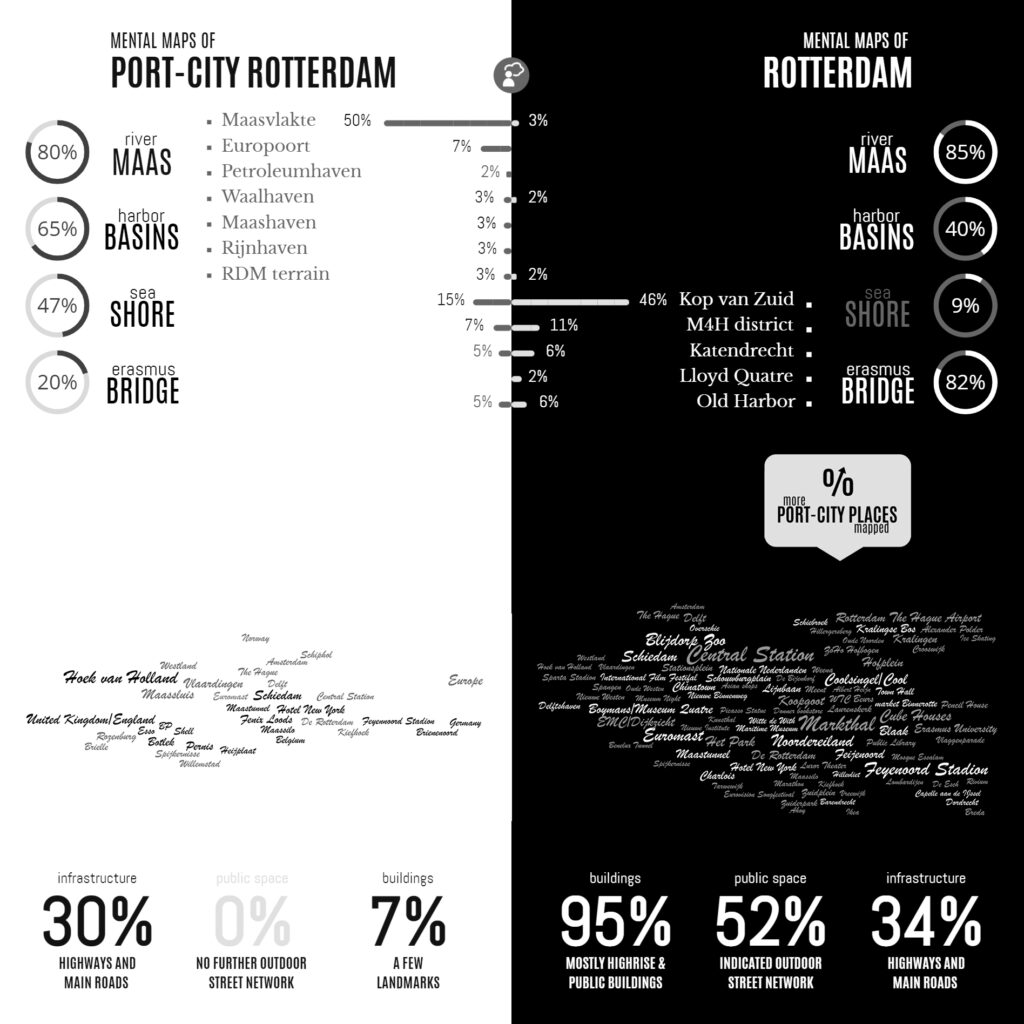
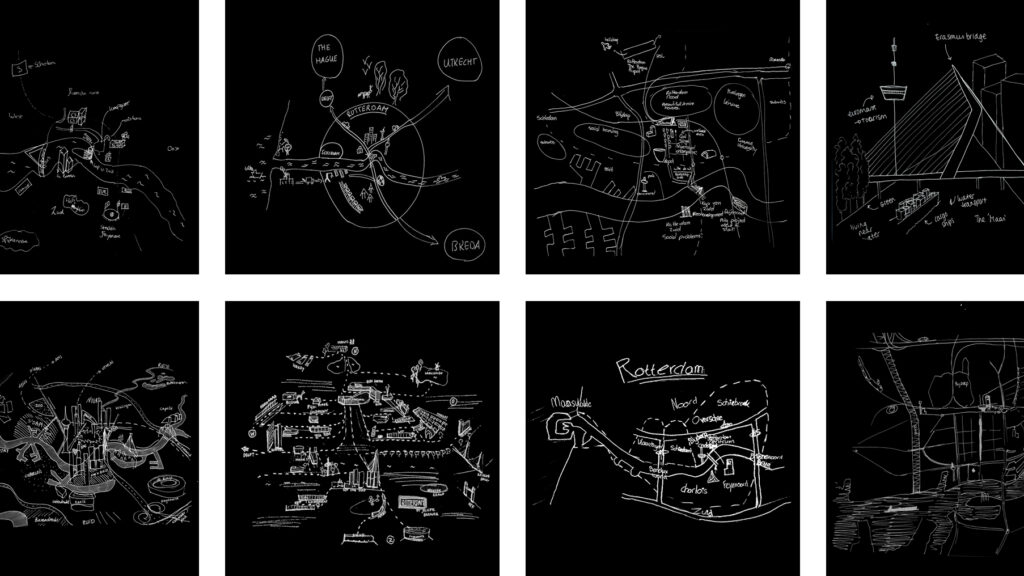
When you cannot find the book you need to understand public space in China, it’s wonderful to see that it is finally written! Wenwen Sun delineates how public space as a Greco-Roman originated concept traversed the urban and architectural cultures of post-reform China, merging and negotiating with the local conditions, and evolved into a new phenomenon in Chinese urban design and architecture. It is hugely rewarding to promote her work!
This research first critically reviews contemporary narratives from Chinese philosophy and sociology, then materials written in post-reform China on the topic of public space. It then analyses various cases in their design and spatial conditions, ranging from ‘shared spaces’ in the areas characterised by urban dwelling and communities to ‘open spaces’ in the central city where strangers mingle and globalisation manifests. By analysing public space as a cultural phenomenon, carrying specific meaning, through specific concepts and designs, this research develops an interpretative framework within which the meanings and transculturation of public space in Chinese urban design and architecture can be understood and elucidates potential for future urban design and architectural practices. Theoretically, it moves beyond the conventional research on public space that is primarily based on Western thoughts, an Indo-European notion, and a Greco-Roman tradition. Practically, it paves the way for future development of the design of public space, highlighting the cultural, social, and spatial dynamics in Chinese cities vis-à-vis the related political, economic, and governmental conditions within the context of ongoing globalisation.
Chinese Notions of Public Space: Transculturation in Urban Design and Architecture after the ‘Reform and Opening-up’ in 1978 Read for free, and order a hard copy here