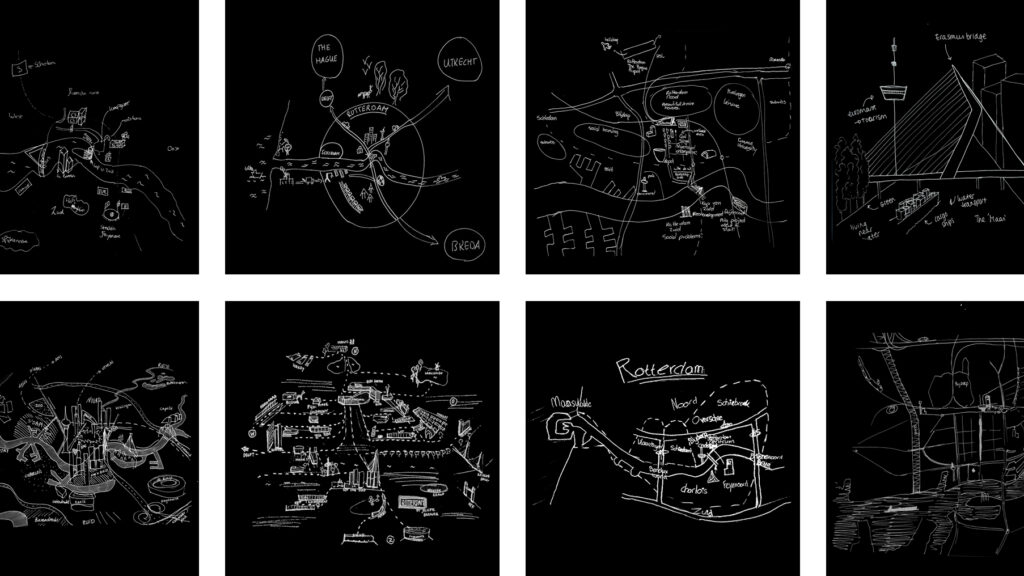
Images of Port-City Rotterdam, through the Mental Mapping Methods
This article makes explicit why, at first, we do not usually think beyond water, docks, cargo, moving loads, and ships when we think of port-cities. By reviewing mental maps of port-city Rotterdam drawn by professionals in training, it becomes clear that the adjective ‘port’ modifies the meaning of ‘city’ in such an extent that this echoes in the mind. It does exceptionally when respondents are asked explicitly to draw the ‘port-city’ by mind. Port and city seem to have become conceptual dichotomies. In the case of Rotterdam, the established professional points of views seem to be aligned with this disunion, even though the current trend in practice turns towards a desire to (re)develop the port-city as one. Through similar mental mapping experiments on Rotterdam, yet without adding the label of ‘port-city’ in the question, much richer images of the port-city of Rotterdam are generated. Multi-scalar reviews of such maps help to explicate much more inherited relations between nature and artifice, as well as for example the flows of goods and people. Ultimately, this approach changes the perspectives on the port-city, also for professionals in practice.
Read:
Harteveld, Maurice (2021b) Images of Port-City Rotterdam, through the Mental Mapping Methods. In: Portus, the Online Magazine of RETE (Association for the Collaboration between Ports and Cities), No. 42-2021, Year XXI. RETE Publisher, Venice, ISSN 2282-5789
See also:
Biographies of Places
Port-City Perspectives
