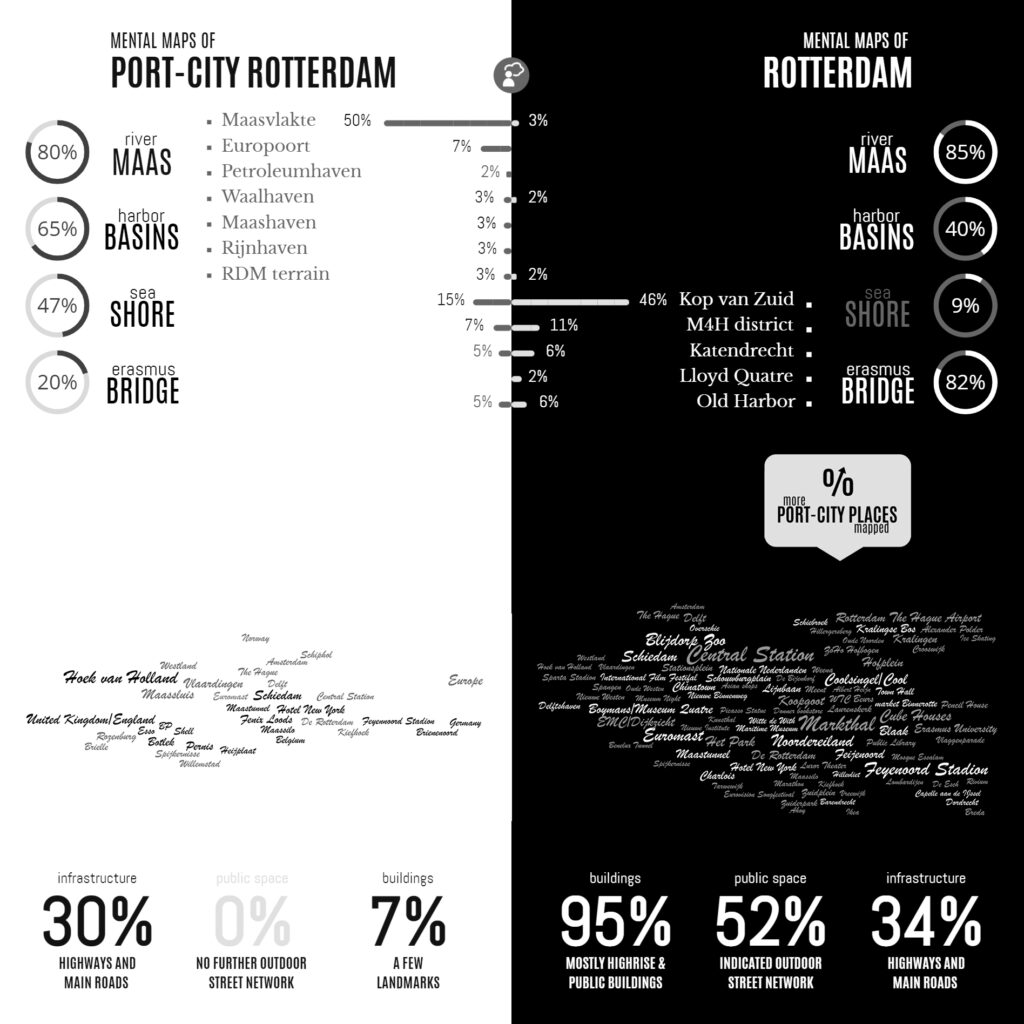
Imagine: You are walking in a public space, and you are using your navigation app to meet at a place, which your friends suggested a few seconds ago on WhatsApp. Your headset is on. Noise is reduced. While walking, you’re traced and tracked; the shortest and fastest route is recalculated continuously, In the mean, a health app may record your cycles, Spotify remembers your music preferences, many other web-data fuel the algorithms, …and synchronically all kinds of devices around you sense your environment too. Every detail is collected for third-parties. Also webcams and what looks like cctv register where you are. They monitor your moves and avoid the unexpected to happen. This morning, the weather app has announced rain. Indeed, while clouds make it shimmer, your smart screen illuminates, and lamps turn on.
You’re still walking… People don’t walk close. This makes you think of what you have read this morning: In some cities, drones are measuring social distance, today, and if too close, through image recognition big brother sends you a fine. – In the mean, a car is passing by smoothly. Your mind links it to the lecture on self-driving vehicles. They are keeping distance automatically… “Who is behind the wheel, btw?” You can’t see. Humanoids, perhaps…? Anyways.
Back to your walk. You have to pay attention for a minute to the surrounding, while you are crossing a street. (Small sensors, have made traffic lights turn green for you.) You are starting to be curious to the place where your friends are waiting. They have been involved in the redesign of this meeting space. Some years ago, one would outline public spaces with computer-aided design. You remember how outcomes have always been presented in ‘sunny’ artist impressions. But, during its realisation, budget restrains always made such a plan somewhat more realistic… Today is a different world. Tools are innovating, and include components ranging from environmental analysis to robotic control. The old outlines may still work… Yet, simulations of human behaviour in space helps to understand complexity. The design of public space can be informed more accurately by our updated models, and digital twins. Automation and print-on-demand can still make old dreams happen. You have seen new video presentations of the place, where you’re heading to, on the internet; they are quite realistic. You’re convinced as a designer, your imagination benefits the people, but alike your friends, nobody is alone in design. Online meetings are integrating viewpoints of other experts and novice users. Webinars are bringing people, ideas, and living rooms, closer together. It may be enriching. Yet, the design of your friends may never be finished. Invitations by Zoom, Meets, Facetime, Webex, Slack, Trello, Miro, Messeger, or Teams are following up. #multionline #haveitall – Also, participatory platforms have invited as many users as possible, to join VR sessions and visit the augmented space, to be. Some of the users have replied and have worked within the framework of your friends, their concept of the future. But for some it was not enough… On Insta, some users have found a better idea. As pro-active citizens, they have organised themselves on social media, via transnational networks and microblogging they have got more inspiration. Tutorials have helped them to learn the trick. Public space design changes in a kind of grassroots development, including peer-2-peer exchange of probably two unfamiliar neighbours. The one simply likes gardening, the other orders always outdoor stuff on discount pages. The pro-active group of users co-create and make the space theirs.
Thoughts fade away; You’re still walking…. Happy you. You are almost there, at the meeting place, where everybody seems active. You see your friends coming near. It’s a really nice place. Not as slick as you thought before, but you like it! “We would have liked to introduce a moving beam here…” on of your friend says: “People would love to sit on such a thing, really.” “It adjusts its position and form in accordance to their moods and likes”, the other adds… – You reply dry: “This bench works for me too”. While you are scanning the surrounding facades for heritage details, your friends starts to discuss hyperrealities, and phygital spaces …endlessly. In the mean, you are distracted by a piece of planting in front of you. It is a bid unorganised, and it seems organically grown, obviously added by the community. It looks like one of those greens, which you must have seen in ‘Spaceship Earth’, the movie, which you screened on your laptop, pay-per-view, during the opening night of the Architecture Film Festival Rotterdam, last month. After a long chat on the ‘future on being’, you really want to leave again. Your eyes are dry and your mind is tired. You are suggesting to play more together next time and relax a bit. You have heard that they have launched a brilliant new ‘massive multiplayer online role-playing game’ Then everybody leaves, and walks away
This is the end of my story…
What do you think: How have you listened to the story: Have you been walking and talking in reality? Or was it your avatar in cyberspace? Near everything in this story is out there. It affects your profession everyday as an designer. Everything is existing as real space as well as virtual space
This story is recorded with a live audience via YouTube on Friday, November 5th, 2.00 – 9:00am CET. – The webinar has been part of the initiative the POLIS Urbanism and Landscape Architecture Week, of Polis