How to Design Public Space for Maritime Mindsets? That’s a central question in the new Minor ‘Minor (Re)Imagining Port Cities: Understanding Space, Society, and Culture’.
Tag Archives: real cities
Designing Domestic Places
| Public space is the place to play, move and meet. This applies to our rich city center with all its shops and restaurants, but just as much to residential areas. But how can we make these public spaces even more attractive for all types of users? At the beginning of February, students from TU Delft, The Hague University of Applied Sciences, and Inholland University of Applied Sciences developed various ideas for the public space in the Tanthof district. In various teams, the students have investigated how existing routes or routes to be designed can be provided with ‘stopping points’: places where you can rest for a while, look around and chat with other residents. During this meeting of Delft Design, these design sketches will be briefly explained and we would like to discuss these design sketches with you and, among others, Tako Postma (City Architect of Delft), Eveline Berghout – van der Schee (urban designer, City of Delft), Maurice Harteveld (researcher, Design of Public Spaces, TU Delft), Ben Kuipers (landscape architect) and Flip Krabbendam ( architect) in a discussion about the preconditions for successful public space. The discussion starts with a lecture on Designing Domestic Places by Maurice Harteveld Afterward, there is an opportunity to chat and view the different designs. This while enjoying a snack and drink. The challenge is organized by Delft Design in collaboration with the City Deal Kennis Maken Delft, study association POLIS and architect Flip Krabbendam. | De openbare ruimte is dé plek voor spelen, bewegen én ontmoeten. Dat geldt voor onze rijke binnenstad met al zijn winkels en horeca, maar even zo goed voor woonwijken. Maar hoe kunnen we deze publieke ruimten nog aantrekkelijker maken voor alle type gebruikers? Begin februari hebben studenten van de TU Delft, De Haagse Hogeschool en Hogeschool Inholland verschillende ideeën uitgewerkt voor de openbare ruimte in de wijk Tanthof. In verschillende teams hebben de studenten onderzocht hoe bestaande of nieuw te ontwerpen routes kunnen worden voorzien van ‘halteplaatsen’: plekken waar men even kan uitrusten, kan rondkijken en een praatje kan maken met andere bewoners. Tijdens deze bijeenkomst van Delft Design worden deze ontwerpschetsen kort toegelicht en gaan we graag met u en onder andere Tako Postma (stadsbouwmeester van Delft), Eveline Berghout – van der Schee (stedebouwkundige. City of Delft), Maurice Harteveld (onderzoeker, Design of Public Spaces, TU Delft), Ben Kuipers (landschapsarchitect) en Flip Krabbendam (architect) in gesprek over de randvoorwaarden van succesvolle openbare ruimte. De discussie wordt geopend met een lezing over Het Ontwerpen van Huiselijke Plekken door Maurice Harteveld Na afloop is er gelegenheid tot napraten en het bekijken van de verschillende ontwerpen. Dit onder het genot van een hapje en drankje. De challenge wordt georganiseerd door Delft Design in samenwerking met de City Deal Kennis Maken Delft, studievereniging POLIS en architect Flip Krabbendam. |
The Public Space as Meeting Place
De Openbare Ruimte als Ontmoetingsplek
where:
Prinsenkwartier en online
when:
2 March 2020
open 19.30, start 20.00 untill 22.00
Design Challenge for Students
City Deal ‘Kowlegde Making Delft’ is organising a challenge about the use and design of public space for ambitious students who would like to push their boundaries. How can we make the public space more attractive for all types of users as a place to play, move and to meet?

More: Design Challenge: Public Space as a Meeting Place
Partners:
the Municipality of Delft
The Hague University of Applied Sciences
Inholland University of Applied Sciences
Delft University of Technology
Delft Design
Biographies of Places
Today, historiographies seem to have moved away from traditional political and diplomatic histories describing cities towards social and cultural approaches. In general, this current shift of interest follows a Late-Modern turn toward the marginalized and marginalizing evidence, and thus explicit hypotheses are tested, and, among others, unbiased data is collected by current biographers. Still, certain narratives stay manifest. Also in Rotterdam. Here, bifocal narratives on the world port and the cosmopolitan city, and the dichotomy among these territories, remain persistent in the most recent biographies. What is seen in everyday space does not match this ontology generally applied in Rotterdam. To greater extent, as such, the samples of the biographies of public spaces as places help to fulfill the most essential public function of researching and abiding justification, while reinvigorating the critical public present in spaces. By opening up to the multiplicity of narratives, the article ‘The Port-City Portrayed in its Public Spaces: Introducing Micro Biographies of Places’ is able to focus on descriptions of Rotterdam which fall outside the scope of the current conventional. Through the lens of ‘biographies of places’, this study particularly follows the so-called material turn, in difference to stories of lives or narratives on actor networks. Hence buildings and artifacts placed in context, are the principal unit of analysis, for a multidimensional interpretation of urban sites across regions and periods.
The approach is operationalized by linking the urban and architectural design of public space, with studies of urban history, literature, cartography, and other urban humanities. This integrated perspective on port-cities is put forward most recently in a wider variety of projects at the LDE Centre of PortCityFutures, which has been promoted and supported for the approach below.
Harteveld, M.G.A.D. (2021) The Port-City Portrayed in its Public Spaces: Introducing Micro Biographies of Places. In: PortusPlus: the Journal of RETE (Association for the Collaboration between Ports and Cities). Venice: RETE, Vol. 12.
See also:
Port-City Perspectives
Maritime Mindsets
Port-City Perspectives
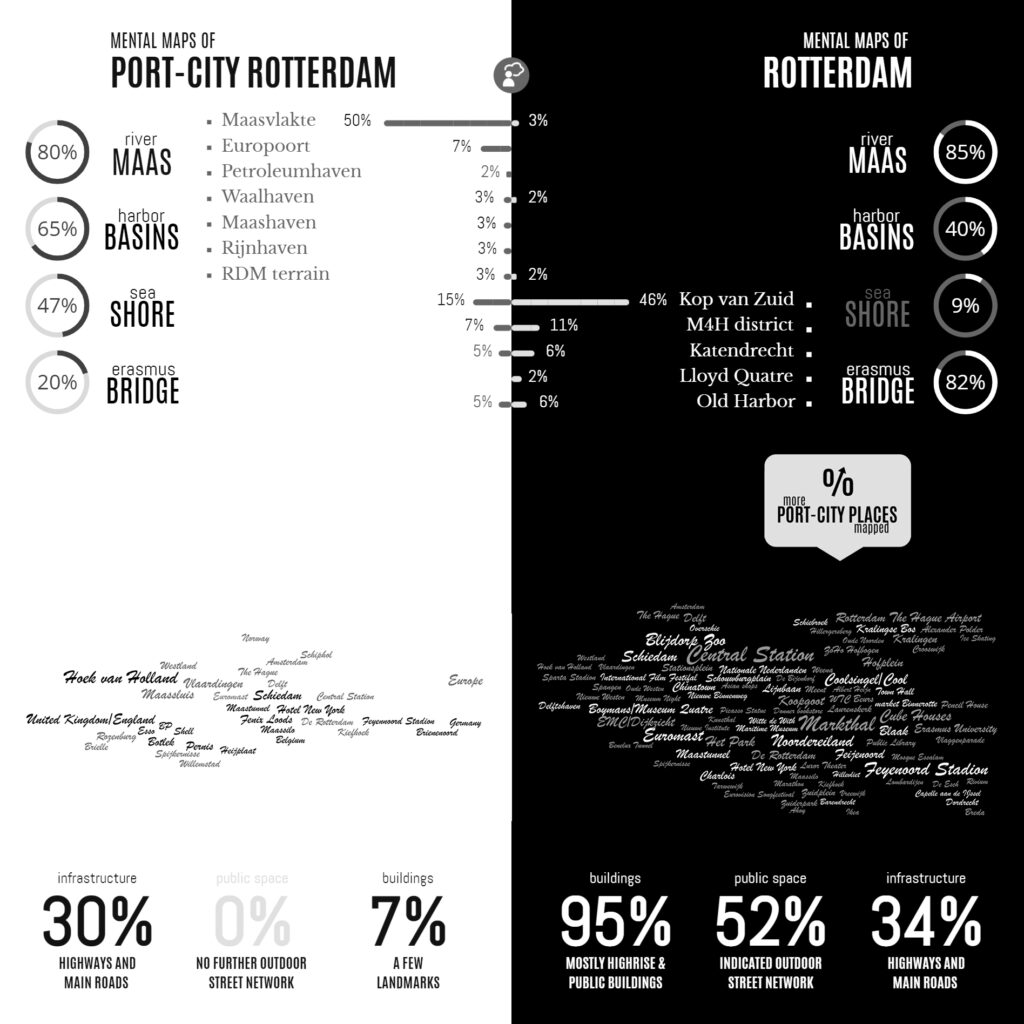
Infographic of the Comparative Analyses on the two Sets of Mental Maps
In the Minds of People: The Case of Rotterdam
Following the geographical ‘Any-Port Model’, urban design has stipulated and enforced the disunion of port and city over the recent decades. In conjunction with other disciplines, the emphasis has been laid at the dislocation of production activities in favour of logistic-productive dynamics. At the same time, the professional focus was on the urban areas where most citizens are. While this practice has led to the redevelopment of abandoned harbour areas too, foremost the approach stimulated stronger physical boundaries between lived city and the remaining and new harbour areas. This article describes the application of the dominant model in Rotterdam over the recent decades, on the basis of literature review, and, it confronts this with the concepts of Rotterdam which are in the minds of professionals-in-training, through the method of ‘mental mapping’. On the one hand, mainly harbour areas are memorised when respondents are asked to draw the port-city of Rotterdam, even though its efficient port infrastructure makes public space in these areas rare, and most harbours are located behind inaccessible borders. On the other hand, civic areas, which have a refined network of public spaces and are places for daily life, reveal also all kinds of tangible and intangible signs and symbols related to characteristics of the port-city when memorised; even more. Various elements, linked to water-land or the flows of goods, people, and ideas, dominate the minds of the people when they think of Rotterdam in general. These outcomes reconfirm the unique unity of port and city and provide a way to find an alternative or supplementary model accepting the complex nature of port-cities.
Read:
Harteveld, Maurice (2021) In the Minds of People: Port-City Perspectives, The Case of Rotterdam, In: European Journal of Creative Practices in Cities and Landscapes (CPCL), Vol. 4, No. 2.
See also:
Maritime Mindsets
Biographies of Places
Stress Reduction and Healing
Rosalie Moesker, an urban designer in training in our team, makes the cross-over to health. As the campus of Erasmus Medical Centre densifies, not only accessibility is at stake, more so, the human experience while traveling. In the city of the future, the medical centre needs new mobility concepts. When we design for these, we can relieve users of worries by reducing urban stress at their arrival, and rethinking public space as a healing environment during stay.
source: TV Rijnmond, Tuesday, November 16, 17:35
Continue reading
Empowering Resilient Communities
Resilient Communities | Comunità Resilienti
Following earlier presentations of the Design of Public Space research group from Delft, Maurice Harteveld participates in the ‘Empowering Resilient Communities’ event organised at the Italian Pavilion at the 14th International Architecture Exhibition in Venice, on Friday 12 November, from 2 pm. As part of the international scientific committee of the pavilion, he will reflect on various Italian projects, which will be presented in this session. His review relates to a broader inventory of actions, which are being currently taken in the networks of public space to strengthen community resilience. Rotterdam serves as an exemplar, and as such these actions challenge the design of public space, and with that among others the disciplines of urban design, landscape architecture, and architecture.
The Italian Pavilion has organised the event as an opportunity to present and discuss some of the experiences already included in the research project Mapping Resilient Communities, while providing a platform for knowledge transfer and capacity development, especially in most vulnerable areas, in Italy and beyond, with the participation of UN-Habitat.
when:
Friday 12 November
14:00-17:00h
where:
17th International Architecture Exhibition
Italian Pavilion
Venice
Continue reading
Expo SubTerra
New Roots for Underground Urbanism – Exhibition

photo by Joran Kuijpers
City x Space: Cross-Section Thinking
How can the integral and multifunctional use of public space, subsurface, and buildings -within a densified urban environment – create space and value that contribute to an attractive and future-proof living environment?
“This seminal question generates various answers depending on the specific context and location of asking. International interdisciplinary students from Delft University of Technology have outlined various design solutions. Manifest in all cases are the spatial bottlenecks on the level of public space. Connecting the intervention areas with the surrounding socio-spatial networks, therefore, forms the basis of all solutions. In addition, in the densification challenges we see the attention for the multi-layered space: on the one hand, a train or metro station, for example, generates flows of people at several levels; on the other hand, building in higher densities and/or living and working in collectives, generates new shared spaces.” As Maurice Harteveld explains in the exhibition; “The hybridization of the urban and architectural program also requires a cross-section thinking. This can be seen in future-proofing both large-scale sports or industrial areas, as well as small-scale residential houses in neighborhoods where work is shifting to local entrepreneurs and home workers. Finally, the subsurface plays an important role in greening the living environment and in water storage.”
Continue reading
Shaping Resilient Communities
Resilient Communities | Comunità Resilienti
With the event, the Italian Pavilion aims to raise awareness on urban resilience, from the environmental, economic, and social point of view, in relation to the 17 Sustainable Development Goals of the 2030 Agenda, on the occasion of Urban October promoted by UN-Habitat. The event has also been scheduled on the occasion of the UN75 celebrations before the Venice Biennale was postponed last year due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
An expert from the Joint Research Center of the European Commission will introduce the Agenda 2030, and invited Italian speakers will present case studies, which already are included in the research project Mapping Resilient Communities – co-created by professionals and urban activists who have experimented and implemented multidisciplinary practices of resilience in Italy and abroad. The event includes a thematic session coordinated by TU Delft, Netherlands, with professors and students affiliated to the Design of Public Spaces Research Group. Finally, a round table discussion is planned with the involvement of the audience attending the live streaming.

when:
Friday 6 October
14:00-17:00h
where:
17th International Architecture Exhibition
Italian Pavilion
Venice
Continue reading
500 Days at Home
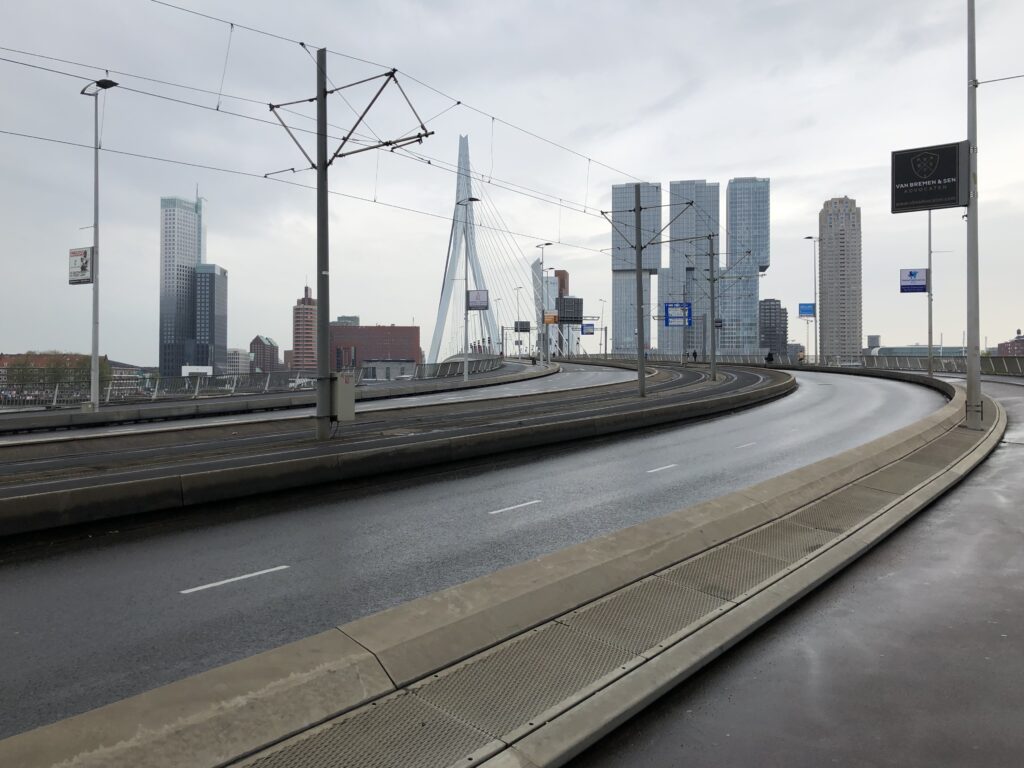 Deserted public space in Rotterdam, the Netherlands. Image by Maurice Harteveld.
Deserted public space in Rotterdam, the Netherlands. Image by Maurice Harteveld.
“After working from home for more than five hundred days, our daily lives and rituals have been severely changed by the COVID-19 pandemic. Moreover, social distancing and other measures have affected everyone’s access to public space and exposed a range of impacts on different levels. Researchers from more than twenty universities explore those impacts in the new open-access publication ‘2020: A Year without Public Space under the COVID-19 Pandemic’.
The crisis in early 2020 immediately brought together the global community of experts on the design of public space. Maurice Harteveld (Urbanism) is part of the scientific board of the Journal of Public Space and distinctly remembers how the initiation of lockdown upon lockdown sparked debate: “Chief editor Luisa Bravo was already in lockdown in the north of Italy, another colleague soon followed in Hong Kong. The progressively worsening health situation led to images of abandoned public space. We started to share local insights, forming a global perspective on the issues arising from the pandemic for the current situation of public space. By connecting with UN-Habitat, the United Nations Human Settlements Programme, this became an opportunity to re-think how cities should be.”Deserted public space in Rotterdam, the Netherlands. Image by Maurice Harteveld.
Health Disparity, Public Space Restrictions and the Future of Public Space
Shared online initiatives resulted in experts from across the world exchanging experiences of care, solidarity, entrepreneurship, academic perspectives, artistic interpretations, and creative practices of human resilience. The resulting key learnings from the early stage of the pandemic are encapsulated in the publication. The research addresses questions like how we can prepare for the consequences of this unprecedented emergency, particularly health disparity, but also addresses the impact of public space restrictions. More generally, the learnings reflect on what the future of public space might be.
At first glance, the challenges for each urban region might look different. Harteveld: “I vividly remember how Casper Chigama, a community developer from Zimbabwe gave an online presentation from his car, addressing how the local concerns there were about how social distancing might be achieved in the short term. But in the long term, pre-existing concerns on urban hygiene were the main challenge. Another colleague from New York City, Setha Low, mentioned how, even with urban hygiene relatively well organised, she still noticed disparity in access to qualitative public space between different population groups of the city.” In the end, the solutions to these challenges might lie within the same realm of making public space more recognisable on a local scale. People should not only have access to public space from their own homes, they should also be able to identify themselves with these places. “We stay closer to home, shown by trends like the increase of working from home and online shopping, and the consecutive decrease of commuting and going to the city centre,” explains Harteveld. “We clearly saw this in 2020, but the trend already emerges in the 1980s. Today, that means we need to be able to feel at home within the public space. As designers and planners of urban space, we can actively contribute to the detailing and programming of the public space to make such attachments possible.” Harteveld calls this the ‘domestication’ of public space. Fellow researchers observe the same, also at places where urban hygiene and inequality is of urgent concern. Josephine Mwongeli Malonza mentions for example how neighbourhood streets function as public space in Kimisange, Rwanda. The future of public space is local, equitably accessible, and very much an interesting and continuing challenge for urban designers, planners, legislators, and other city dwellers.”
#500Days @Home
The 500th day at home passed by on Monday 19 July, 2021
Published:
2020: A year without public space
July 2021
